How Long Is an Eon
As we look up at the stars and ponder the vastness of the universe, it’s easy to feel small and insignificant. But as inhabitants of planet Earth, we are part of a story that spans billions of years. This story is divided into eons, each representing a significant period in our planet’s history. But just how long is an eon? In this article, we will explore the definition of an eon, the history of Earth’s eons, how their length is measured, and what the future holds for our planet’s eons. By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of just how long an eon truly is and how it fits into the grand narrative of our universe.
Defining an Eon
When we talk about the history of our planet, we often use the term “eon” to describe vast stretches of time. But what exactly is an eon? Simply put, an eon is a unit of geological time that spans billions of years. It’s the largest division of time on the geological timescale, and it’s used to describe the major periods in Earth’s history.
Eons are divided into eras, which are further divided into periods and epochs. Each eon represents a significant change in the Earth’s geological and biological history. For example, the Precambrian eon covers the first 4 billion years of Earth’s history, during which life first emerged and evolved into complex organisms. The Phanerozoic eon, which began around 540 million years ago and continues to this day, is characterized by the emergence of multicellular life forms and the evolution of species we recognize today.
Understanding what an eon is helps us appreciate just how long these periods of time really are. It can be difficult for us to wrap our minds around billions of years, but by breaking down Earth’s history into manageable chunks using units like eons, we can better understand how our planet has changed over time.
The History of the Earth’s Eons
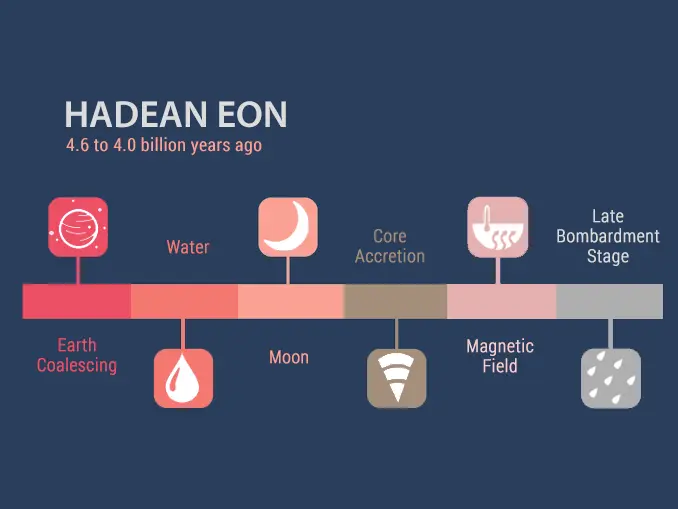
The history of the Earth’s eons is a fascinating subject that takes us back billions of years. The Earth has gone through several eons, each marked by significant geological and biological events. The first eon was the Hadean Eon, which began with the formation of the Earth about 4.6 billion years ago and lasted until about 4 billion years ago. During this time, the Earth was still in its molten state, and there were no life forms on it.
The second eon was the Archean Eon, which lasted from about 4 billion to 2.5 billion years ago. This eon saw the emergence of life on Earth in the form of single-celled organisms such as bacteria and archaea. The Proterozoic Eon followed, lasting from about 2.5 billion to 541 million years ago. This eon saw the evolution of complex life forms such as multi-cellular organisms like algae and jellyfish.
Finally, we have our current Phanerozoic Eon, which began about 541 million years ago and continues to this day. This eon is marked by an explosion of biodiversity with the emergence of animals such as fish, reptiles, birds, mammals, and eventually humans. Understanding these different eons helps us appreciate how much our planet has changed over time and how life has evolved to adapt to those changes.
The Length of an Eon
When we talk about the length of an eon, it’s important to note that we are dealing with a vast expanse of time. An eon is one of the largest units of geological time, and it is typically measured in millions or billions of years. In fact, an eon is so long that it can be difficult for us as humans to truly comprehend its scale.
To put things into perspective, consider this: the current eon that we are in, known as the Phanerozoic Eon, began around 541 million years ago. That means that all of human history – from the earliest civilizations to modern times – represents just a tiny fraction of this eon. And even within the Phanerozoic Eon, there have been three major eras (the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic), each lasting hundreds of millions of years.
So when we talk about how long an eon is, we are talking about a truly mind-boggling amount of time. But despite its enormity, studying these vast stretches of geological time can help us better understand our planet’s history and evolution over billions of years.
Measuring the Length of an Eon
When it comes to measuring the length of an eon, scientists use a variety of methods. One common way is by studying the rock layers on Earth’s surface. Each layer represents a different period in the planet’s history, and by analyzing the fossils and other materials found within them, scientists can determine when each layer was formed.
Another method is by studying isotopes, which are variations of elements with different numbers of neutrons. By measuring the decay rate of certain isotopes, scientists can determine how long ago they were formed and use that information to estimate the length of an eon.
While these methods provide valuable insights into Earth’s history, they are not always precise. Eons can span millions or even billions of years, making it difficult to measure their exact length. Nonetheless, by combining multiple lines of evidence and using sophisticated analytical techniques, scientists continue to refine their understanding of Earth’s eons and how they have shaped our planet over time.
The Future of the Earth’s Eons
As we look towards the future of the Earth’s eons, it’s important to consider the impact that human activity has on our planet. The current epoch, known as the Holocene, began roughly 11,700 years ago and has been marked by a relatively stable climate that has allowed for the growth and development of human civilization. However, with the onset of the Anthropocene – a proposed new epoch characterized by significant human influence on the Earth’s systems – there are concerns about how this will affect future eons.
One potential outcome is that human activity could significantly shorten or even halt the progression of future eons. For example, if we continue to emit greenhouse gases at current rates and fail to address climate change, we could trigger a mass extinction event that would mark the end of the current Phanerozoic eon. On the other hand, if we take action to mitigate our impact on the planet and work towards sustainable practices, we may be able to ensure that future eons continue to unfold in a way that supports life on Earth. Ultimately, it is up to us as a species to determine what kind of legacy we leave behind for future generations and for the planet itself.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of an eon is a fascinating one that has been shaped by the history of our planet. The Earth’s eons have spanned billions of years and have seen incredible changes in the planet’s climate, geography, and life forms. While it may be difficult to comprehend such vast amounts of time, scientists have developed methods for measuring the length of an eon and understanding how they fit into the larger picture of Earth’s history. As we look to the future, it is clear that our planet will continue to evolve and change over time, with new eons yet to come. Understanding these processes can help us better appreciate the incredible complexity and beauty of our world.






